Conference Information
About us
PULSUS Group is pleased to invite you to participate in the “3rd International Conference on Lasers, Optics & Photonics” during November 14-15, 2018 at San Antonio, USA, which will integrate keynote presentations, Oral talks, Poster presentations and Exhibitions and special discussions on wide range of session themes on Laser, Optics and Photonics. It will bring together a collection of investigators who are at the forefront of their field and will provide opportunities for junior scientists and graduate students, researchers and other delegates to interactively present their work and exchange ideas with established senior scientists.
Optics-Photonics 2018 has been designed in an interdisciplinary manner with a multitude of tracks to choose from every segment and provides you with a unique opportunity to meet up with peers from both industry and academia and establish a scientific network between them. We cordially invite all concerned people to come join us at our event and make it successful by your participation.
PULSUS Group. is an internationally renowned peer-review publisher in scientific, technical, and medical journals established in the year 1984 with offices in Ontario, Canada and Hyderabad, India has acquired Andrew John Publishing and openaccessjournals.com to expand its Open Access Publishing through its 50+ journals in association with 20+ International medical and scientific societies.
At PULSUS Group, It is our ideology to bring maximum exposure to our attendees, so we make sure the event is a blend which covers professionals such as Physicists, Academic Scientists, Radiologists, and Dentists from academia & industry making the Optics-Photonics 2018 conference a perfect platform.
The conference will be organized around the Theme ‘A New Era towards Lasers, Optics & Photonics Technologies’. Our goal is to deliver an outstanding program which covers the entire spectrum of research & innovations in Laser, Optics and Photonics and share the cross-cultural experiences of various technical innovations.
Attendees can:
Take advantage of opportunities to learn insights about Laser, Optics and Photonics from a variety of oral and poster presentations.
Meet and network with Physicists ranging from students to deans, faculty, and researchers.
Take advantage of opportunities to collaborate with Researchers from around the world.
Attend prominent plenary sessions about relevant issues in the use of laser in Medical field and the recent techniques adapted in Healthcare sector.
Target Audience:
- Physicist
- Radiologist
- Dentist
- Ophthalmologist
- Oncologist
- Cosmetic Surgeons
- Professors
- Academic Scientist
- Students
- Researchers
- Astronomist
- Laser Technician
- Directors, Managers and CEO
- Brand Manufacturers/ Marketers of Consumer Products
- Marketing, Advertising and Promotion Agency Executives
Tracks/Sessions
PULSUS extends its invitation to welcome “International Conference on Lasers, Optics & Photonics” during November 14-15, 2018 at San Antonio, USA with the theme “A New Era Towards Lasers, Optics & Photonics Technologies”
Laser Systems
LASER stands for light amplification by stimulated emission of radiation. We all know that light is an electromagnetic wave. Each wave has its own brightness and colour, and vibrates at a certain angle, called polarization. This theory also applies to laser light but it is more parallel than any other light source. Every part of the beam has almost exact same direction and so the beam will diverge very little. With a good laser an object at a distance of 1 km can be illuminated with a dot about 60 mm in radius. As it is so parallel, it can be focused to very small diameters where concentration of light energy becomes so high that you can drill, cut, or turn with the ray. It is also possible to illuminate and examine very tiny details with the lasers, thus it is used in surgical applications and CD players as also. It can also be made very monochromic, thus only one light wavelength is present. This is not the instance with the ordinary light sources. White light contains all colours in the spectrum, but even a coloured light, such as a red LED contains a repeated interval of red wavelengths.
Optics Congress | Physics Congress | Laser Congress | Photonics Congress
Related Societies: American Physical Society | Fellows of the Australian Institute of Physics | Institute of Physics | Optical Society | Académie de Physique | American Crystallographic Association | American Physical Society | Australian Institute of Physics | Austrian Physical Society | Brazilian Physical Society | Canadian Association of Physicists | Chinese Physical Society | Community of Physics | Deutsche Physikalische Gesellschaft | Estonian Physical Society | European Physical Society | Faraday Society | Indian Physical Society | Institute of Physics | Italian Physical Society | International Association of Mathematical Physics | International Society on General Relativity and Gravitation | Italian Society for General Relativity and Gravitation | Japan Society of Applied Physics | Nepal Physical Society | The Optical Society | Photonics Society of Poland | Physical Society of London | Swiss Physical Society | Physics Society of Iran | Société Française de Physique | Society of Physicists of Macedonia | Society of Physics Students | Mathematical Association of America
Optics and Lasers in Medicine
There are some surgical operations that are perplexing to perform with the conventional scalpel. Initial trials with laser beam showed that a finely focused beam from a carbon dioxide gas laser could cut through human tissue effortlessly and neatly. The surgeon could direct the beam from any angle by using a mirror attached on a movable metal arm. Therefore, now a day’s laser beam is the most desirable tool which is used as a standby for the conventional blade to perform difficult surgeries. Lasers were considered as most effective in operating on parts that are easy to reach-areas on the body's exterior, including the ears, skin, mouth, eyes and nose. But in recent years doctors have established the remarkable progress in emerging laser techniques for use in internal exploration and surgery. For illustration lasers are gradually used to clean plaque from people's arteries.
Optics Congress | Physics Congress | Laser Congress | Photonics Congress
Related Societies: Society of Physicists of Macedonia | Society of Physics Students | Mathematical Association of AmericAmerican Physical Society | Fellows of the Australian Institute of Physics | Institute of Physics | Optical Society | Académie de Physique | American Crystallographic Association | American Physical Society | Australian Institute of Physics | Austrian Physical Society | Brazilian Physical Society | Canadian Association of Physicists | Chinese Physical Society | Community of Physics | Deutsche Physikalische Gesellschaft | Estonian Physical Society | European Physical Society | Faraday Society | Indian Physical Society | Institute of Physics | Italian Physical Society | International Association of Mathematical Physics | International Society on General Relativity and Gravitation | Italian Society for General Relativity and Gravitation | Japan Society of Applied Physics | Nepal Physical Society | The Optical Society | Photonics Society of Poland | Physical Society of London | Swiss Physical Society | Physics Society of Iran | Société Française de Physique
Optoelectronics
Optoelectronics is the field of technology that associates the physics of light with electricity. It incorporates the design, study and manufacture of hardware devices that convert electrical signals into photon signals and photons signals to electrical signals. Any device that operates as an electrical-to-optical or optical-to-electrical is considered an optoelectronic device. Optoelectronics is built up on the quantum mechanical effects of light on electronic materials, sometimes in the presence of electric fields, especially semiconductors. Optoelectronic technologies comprise of laser systems, remote sensing systems, fibre optic communications, optical information systems, and electric eyes medical diagnostic systems.
Optics Congress | Physics Congress | Laser Congress | Photonics Congress
Related Societies: Mathematical Association of AmericAmerican Physical Society | Society of Physicists of Macedonia | Society of Physics Students | Fellows of the Australian Institute of Physics | Institute of Physics | Optical Society | Académie de Physique | American Crystallographic Association | American Physical Society | Australian Institute of Physics | Austrian Physical Society | Brazilian Physical Society | Canadian Association of Physicists | Chinese Physical Society | Community of Physics | Deutsche Physikalische Gesellschaft | Estonian Physical Society | European Physical Society | Faraday Society | Indian Physical Society | Institute of Physics | Italian Physical Society | International Association of Mathematical Physics | International Society on General Relativity and Gravitation | Italian Society for General Relativity and Gravitation | Japan Society of Applied Physics | Nepal Physical Society | The Optical Society | Photonics Society of Poland | Physical Society of London | Swiss Physical Society | Physics Society of Iran | Société Française de Physique
Optical Communications and Networking
Optical communications networks are enhancing a vital role such as there is high demand for capacity links. DWDM which means dense wavelength division multiplexing is widely deployed at the core networks to deliver high capacity transport systems. Optical components such as, tunable filters, termination devices, optical amplifiers transceivers, and add-drop multiplexers are becoming more trustworthy and affordable. Access network and metropolitan area networks are increasingly built with optical technologies to overcome the electronic blockage at network edges. Subsystems and new components for very high speed optical networks offer a new design options. Free-space optical communication has been arranged in space, while terrestrial forms are naturally limited by weather, geography and the availability of light.
Optics Congress | Physics Congress | Laser Congress | Photonics Congress
Related Societies: Nepal Physical Society American Physical Society | Fellows of the Australian Institute of Physics | Institute of Physics | Optical Society | Académie de Physique | American Crystallographic Association | American Physical Society | Australian Institute of Physics | Austrian Physical Society | Brazilian Physical Society | Canadian Association of Physicists | Chinese Physical Society | Community of Physics | Deutsche Physikalische Gesellschaft | Estonian Physical Society | European Physical Society | Faraday Society | Indian Physical Society | Institute of Physics | Italian Physical Society | International Association of Mathematical Physics The Optical Society | Photonics Society of Poland | Physical Society of London | Swiss Physical Society | Physics Society of Iran | Société Française de Physique | Society of Physicists of Macedonia | Society of Physics Students | Mathematical Association of America | International Society on General Relativity and Gravitation | Italian Society for General Relativity and Gravitation | Japan Society of Applied Physics |
Nanophotonics and Biophotonics
Nano photonics is the study of the behavior of light on the nano meter scale, and of the interaction of nano meter-scale objects with light. It is a branch of optics, electrical engineering, and nanotechnology. It often involves metallic components, which can transport and focus light by means of surface plasmon polaritons. Bio photonics can also be described as the advance and application of optical techniques particularly imaging, to study of biological molecules, tissue and cells. One of the main benefits of using optical techniques which make up bio photonics is that they reserve the reliability of the biological cells being examined, i.e. scattering material, on a microscopic or macroscopic scale
Optics Congress | Physics Congress | Laser Congress | Photonics Congress
Related Societies: International Society on General Relativity and Gravitation | Italian Society for General Relativity and Gravitation | Japan Society of Applied Physics | Nepal Physical Society American Physical Society | Fellows of the Australian Institute of Physics | Institute of Physics | Optical Society | Académie de Physique | American Crystallographic Association | American Physical Society | Australian Institute of Physics | Austrian Physical Society | Brazilian Physical Society | Canadian Association of Physicists | Chinese Physical Society | Community of Physics | Deutsche Physikalische Gesellschaft | Estonian Physical Society | European Physical Society | Faraday Society | Indian Physical Society | Institute of Physics | Italian Physical Society | International Association of Mathematical Physics The Optical Society | Photonics Society of Poland | Physical Society of London | Swiss Physical Society | Physics Society of Iran | Société Française de Physique | Society of Physicists of Macedonia | Society of Physics Students | Mathematical Association of America
Quantum Science and Technology
A quantum sensor is the device that exploits quantum correlations such as quantum entanglement to achieve sensitivity or the resolution that is better than can attain using only classical systems. A quantum sensor can measure effect of quantum state of alternative system by itself. The simple act of measurement influences quantum state and varies the probability and the uncertainty associated with its state during measurement. Quantum sensor is the term used in other settings wherever entangled quantum systems are browbeaten to make better more sensitive magnetometers or atomic clocks. Quantum Photonics is to explore the fundamental features of quantum mechanics and also the work towards future photonic quantum technologies by manipulating, generating and measuring single photons as well as the quantum systems that emit photons. The market for quantum dots-built products such as new television screens is projected to reach $3.5 billion by 2020. The majority of this growth will come from increased demand in the US.
Optics Congress | Physics Congress | Laser Congress | Photonics Congress
Related Societies: Society of Physicists of Macedonia | Society of Physics Students | Mathematical Association of AmericAmerican Physical Society | Fellows of the Australian Institute of Physics | Institute of Physics | Optical Society | Académie de Physique | American Crystallographic Association | American Physical Society | Australian Institute of Physics | Austrian Physical Society | Brazilian Physical Society | Canadian Association of Physicists | Chinese Physical Society | Community of Physics | Deutsche Physikalische Gesellschaft | Estonian Physical Society | European Physical Society | Faraday Society | Indian Physical Society | Institute of Physics | Italian Physical Society | International Association of Mathematical Physics | International Society on General Relativity and Gravitation | Italian Society for General Relativity and Gravitation | Japan Society of Applied Physics | Nepal Physical Society | The Optical Society | Photonics Society of Poland | Physical Society of London | Swiss Physical Society | Physics Society of Iran | Société Française de Physique
Quantum optics
A quantum detector could be a device that exploits quantum correlations, like a quantum trap, to attain a sensitivity or resolution that's higher than will be achieved exploitation only classical systems. A quantum device will measure the impact of the quantum state of another system on itself. The mere act of measure influences the quantum state and alters the likelihood and uncertainty related to its state throughout measuring. The Defense, Advanced analysis comes Agency has recently launched a search program in optical quantum sensors that seeks to use concepts from quantum science and quantum imaging, like quantum lithography and also the noon state, so as to attain these goals with optical sensing element systems like measuring system. Quantum detector is additionally a term utilized in different settings wherever entangled quantum systems are exploited to form higher atomic clocks or a lot of sensitive magnetometers. The marketplace for a quantum dots primarily based product, such as new tv screens, is projected to achieve $3.5 billion by 2020. The bulk of this growth can return from enlarged demand in the United States.
Optics Congress | Physics Congress | Laser Congress | Photonics Congress
Related Societies: Nepal Physical Society American Physical Society | Fellows of the Australian Institute of Physics | Institute of Physics | Optical Society | Académie de Physique | American Crystallographic Association | American Physical Society | Australian Institute of Physics | Austrian Physical Society | Brazilian Physical Society | Canadian Association of Physicists | Chinese Physical Society | Community of Physics | Deutsche Physikalische Gesellschaft | Estonian Physical Society | European Physical Society | Faraday Society | Indian Physical Society | Institute of Physics | Italian Physical Society | International Association of Mathematical Physics The Optical Society | Photonics Society of Poland | Physical Society of London | Swiss Physical Society | Physics Society of Iran | Société Française de Physique | Society of Physicists of Macedonia | Society of Physics Students | Mathematical Association of America | International Society on General Relativity and Gravitation | Italian Society for General Relativity and Gravitation | Japan Society of Applied Physics |
Optical Physics
Optical physics is a study of atomics and molecules. It is the study of electromagnetic radiation, the interaction and the properties of that radiation, with matter, especially its manipulation and control. It differs from general optics and optical engineering, however among optical physics, applied optics, and optical engineering, the applications of applied optics and the devices of optical engineering are necessary for basic research in optical physics, and that research takes to the development of new devices and applications. Major study in optical physics is also keen to quantum optics and coherence. In optical physics, research is also stimulated in areas such as ultra-short electromagnetic fields, the nonlinear response of isolated atoms to intense, quantum properties of the electromagnetic field, and the atom-cavity interaction at high fields
Optics Congress | Physics Congress | Laser Congress | Photonics Congress
Related Societies: International Society on General Relativity and Gravitation | Italian Society for General Relativity and Gravitation | Japan Society of Applied Physics | Nepal Physical Society American Physical Society | Fellows of the Australian Institute of Physics | Institute of Physics | Optical Society | Académie de Physique | American Crystallographic Association | American Physical Society | Australian Institute of Physics | Austrian Physical Society | Brazilian Physical Society | Canadian Association of Physicists | Chinese Physical Society | Community of Physics | Deutsche Physikalische Gesellschaft | Estonian Physical Society | European Physical Society | Faraday Society | Indian Physical Society | Institute of Physics | Italian Physical Society | International Association of Mathematical Physics The Optical Society | Photonics Society of Poland | Physical Society of London | Swiss Physical Society | Physics Society of Iran | Société Française de Physique | Society of Physicists of Macedonia | Society of Physics Students | Mathematical Association of America
Optical Fiber
An optical fiber is a flexible as well as transparent fiber made by silica glass or plastic to a diameter slightly thicker than that of a human hair. Optical fibers are used mostly to transmit light between the two ends of the fiber and widely used in fiber-optic communications, unlike cable wires optical fiber permits transmission over longer distances and at higher bandwidths than wire cables. Instead of metal wires fibers are used because signals travel along them with lesser amounts of loss; in addition to this fiber are also safe to electromagnetic interference, a problem to which metal wires suffer excessively. Specially designed fibers are also used for a various other application, some of them being fiber lasers and fiber optic sensors.
Optics Congress | Physics Congress | Laser Congress | Photonics Congress
Related Societies: International Society on General Relativity and Gravitation | Italian Society for General Relativity and Gravitation | Japan Society of Applied Physics | Nepal Physical Society American Physical Society | Fellows of the Australian Institute of Physics | Institute of Physics | Optical Society | Académie de Physique | American Crystallographic Association | American Physical Society | Australian Institute of Physics | Austrian Physical Society | Brazilian Physical Society | Canadian Association of Physicists | Chinese Physical Society | Community of Physics | Deutsche Physikalische Gesellschaft | Estonian Physical Society | European Physical Society | Faraday Society | Indian Physical Society | Institute of Physics | Italian Physical Society | International Association of Mathematical Physics | The Optical Society | Photonics Society of Poland | Physical Society of London | Swiss Physical Society | Physics Society of Iran | Société Française de Physique | Society of Physicists of Macedonia | Society of Physics Students | Mathematical Association of America
Technologies in Lasers, Optics and Photonics
Lasers emit high-intensity light beams. In laser and optical technologies, professionals channel these beams for use in scientific instruments, engineering, biomedical research, communication and medicine. Furthermore, laser and optical technology can further the fields of medicine.
Optics Congress | Physics Congress | Laser Congress | Photonics Congress
Related Societies: Nepal Physical Society American Physical Society | Fellows of the Australian Institute of Physics | Institute of Physics | Optical Society | Académie de Physique | American Crystallographic Association | American Physical Society | Australian Institute of Physics | Austrian Physical Society | Brazilian Physical Society | Canadian Association of Physicists | Chinese Physical Society | Community of Physics | Deutsche Physikalische Gesellschaft | Estonian Physical Society | European Physical Society | Faraday Society | Indian Physical Society | Institute of Physics | Italian Physical Society | International Association of Mathematical Physics The Optical Society | Photonics Society of Poland | Physical Society of London | Swiss Physical Society | Physics Society of Iran | Société Française de Physique | Society of Physicists of Macedonia | Society of Physics Students | Mathematical Association of America | International Society on General Relativity and Gravitation | Italian Society for General Relativity and Gravitation | Japan Society of Applied Physics |
Applications and Trends in Optics and Photonics
Applications of photonics are abundant. They include in our everyday life to the most advanced science, e.g. information processing, light detection, spectroscopy, telecommunications, lighting, information processing, lighting, metrology, laser material processing, spectroscopy, medicine, military technology, bio photonics, agriculture, robotics, and visual art.
Optics Congress | Physics Congress | Laser Congress | Photonics Congress
Related Societies: International Society on General Relativity and Gravitation | Italian Society for General Relativity and Gravitation | Japan Society of Applied Physics | Nepal Physical Society American Physical Society | Fellows of the Australian Institute of Physics | Institute of Physics | Optical Society | Académie de Physique | American Crystallographic Association | American Physical Society | Australian Institute of Physics | Austrian Physical Society | Brazilian Physical Society | Canadian Association of Physicists | Chinese Physical Society | Community of Physics | Deutsche Physikalische Gesellschaft | Estonian Physical Society | European Physical Society | Faraday Society | Indian Physical Society | Institute of Physics | Italian Physical Society | International Association of Mathematical Physics | The Optical Society | Photonics Society of Poland | Physical Society of London | Swiss Physical Society | Physics Society of Iran | Société Française de Physique | Society of Physicists of Macedonia | Society of Physics Students | Mathematical Association of America
Market Analysis
Summary
Optics-Photonics 2018 welcomes attendees, presenters, and exhibitors from all over the world to San Antonio, USA. We are delighted to invite you all to attend and register for the ” International Conference on Lasers, Optics & Photonics” which is going to be held during November 14-15, 2018 in San Antonio, USA.
The organizing committee is gearing up for an exciting and informative conference program including plenary lectures, symposia, workshops on a variety of topics, poster presentations and various programs for participants from all over the world. We invite you to join us at Lasers, Optics & Photonics 2018, where you will be sure to have a meaningful experience with scholars from around the world.
Importance& Scope:
Optics and Laser Technology is one of the growing fields and scope of Optics and Laser Technology encompasses in several areas such as development in all different types of lasers, development in optoelectronic devices & photonics and development in Optical instruments & components. It has many Medical applications mainly in the field of Ophthalmology, Radiology, Dentistry, and Dermatology and it also has many Industrial applications such as Laser cutting, Laser welding, Laser scribing etc. At present the Laser Technology market is around $7 billion and it is expected to grow up to $17.06 billion by the year 2020.
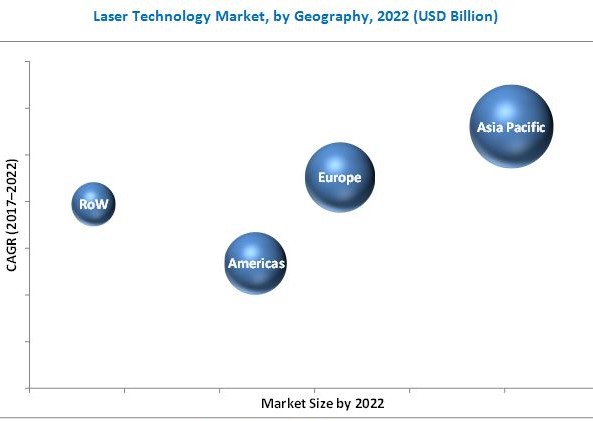
According to the new market research report on the "Laser Technology Market by Type (Solid, Liquid, & Gas), Application (Optical communication & laser processing), Vertical (Commercial, Telecom, Research, Defense, Medical, Automotive, Electronics, & Industrial), & Geography - Global Forecast to 2022", this market is expected to be valued at USD 15.38 Billion by 2022, at a CAGR of 5.2% between 2017 and 2022. The major factors driving the growth of the laser technology market include increasing demand from the healthcare sector and shift towards production of nano and micro devices, and enhanced performance over the traditional material processing techniques.
The global laser diode market is expected to grow at a CAGR of 13.0% between 2015 and 2020. The Asia-Pacific region is expected to dominate the market at a CAGR of 15.0% between 2015 and 2020.The major companies involved in the laser diode market such as Osram Licht Group (Germany), Panasonic Semiconductor Solutions Co., Ltd. (Japan), ROHM Co., Ltd. (Japan), IPG Photonics Corp. (U.S.), Sharp Corp. (Japan), Coherent, Inc. (U.S.), Hamamatsu Photonics K.K. (Japan), JDS Uniphase Corp. (U.S.), Jenoptik AG (Germany), Newport Corp. (U.S.), Rofin-Sinar Technologies, Inc. (U.S.), Finisar (U.S.), Avago Technologies (Singapore), Trumpf GmbH + Co. KG (Germany), and Nichia Corp. (Japan).
The global adaptive optics market is expected to reach USD 7,666.4 Million by 2020, at a CAGR of 99.4% between 2015 and 2020. The military & defense sector was the largest contributor to the overall adaptive optics market, accounting for a share of 56.1% in 2014. The biomedical sector accounted for a share of 21.7% of the market in 2014. The Americas accounted for the largest share of 44.0% of the Adaptive optics market in 2014; it is expected to grow at a CAGR of 94.0% between 2015 and 2020.